Artificial intelligence in healthcare sparks a profound transformation in clinical workflows, diagnostics, treatments, and patient experience. AI in healthcare accelerates data analysis, enables predictive analytics, and reshapes core medical processes. Hospitals and clinics now use AI healthcare solutions to screen radiology scans, flag disease markers, model treatment responses, and monitor patient vitals in real time. This innovation saves lives, cuts costs, and empowers precision medicine for millions globally.
Origins & Early Momentum
The journey of AI concerning healthcare began gaining serious traction in 2011 with IBM’s launch of Watson Health. This groundbreaking AI system leveraged natural language processing (NLP) to interpret vast volumes of medical literature and clinical notes, offering data-driven insights to support medical professionals.
This milestone in healthcare marked the first large-scale application of AI, setting the stage for future innovation. Today, tech giants like Apple, Microsoft, Amazon, and Google are heavily investing in AI healthcare applications, accelerating their integration across diagnostics, patient monitoring, and hospital operations. What began as a niche technology now drives enterprise-wide transformation in modern healthcare systems.

Key AI Technologies Powering Healthcare
• Machine Learning & Deep Learning
Machine learning fuels the majority of AI for the healthcare sector by training algorithms on clinical datasets, allowing them to predict outcomes or detect subtle trends. Deep learning, a subset, handles tasks like image recognition (e.g., MRI, X-ray), speech-to-text for medical records, and discovering novel drug targets. These systems match or outperform human experts in disease detection, while scaling at speed and accuracy .
Benefits of AI in medical diagnosis and treatment surge as algorithms sift millions of records to spot patterns clinicians might miss. Examples include precise oncology therapy recommendations and real-time monitoring of sepsis symptoms.
• Natural Language Processing (NLP)
AI healthcare applications employ NLP to convert clinical notes, PDFs, and electronic health records (EHRs) into structured, actionable insights. NLP captures patient symptoms, medical history, prescriptions, and more. Clinicians gain rapid access to risk factors and relevant care paths—streamlining documentation and reducing diagnostic errors. Role of AI in healthcare management systems emerges clearly: NLP can recommend medication adjustments, suggest EHR codes, and predict patient deterioration—enhancing strategic decisions and patient safety.
• Rule‑based Expert Systems
Although earlier AI present in the healthcare sector relied on if‑then rule engines in expert systems, these have evolved into hybrid solutions. Today, they act as clinical decision support modules within EHRs, endorsing diagnostic suggestions, flagging inconsistencies, or validating medication interactions.
• Diagnosis and Treatment Tools
Modern AI combines machine learning, deep learning, and NLP into end-to-end systems. These tools analyse imaging scans, recommend treatment plans, and flag high-risk conditions. Though integration into hospital workflows and claims processing still challenges AI, many hospitals are adopting third-party modules to overcome these barriers.
AI Healthcare Applications in Action
• Early Disease Detection & Imaging
Artificial intelligence in healthcare excels at early detection in mammography, CT scans, and MRIs. AI detects anomalies—like small tumors—beyond human visibility, reducing screening times while increasing accuracy.
• Personalised Medicine & Drug Discovery
Precision medicine thrives with AI. Algorithms analyse genomic data, biomarkers, and treatment history to tailor therapies. In pharmacy, artificial intelligence accelerates drug discovery by modelling molecular interactions and automating formulation—slashing development time and costs.
• Remote Patient Monitoring
AI‑powered remote monitoring uses wearable sensors and smart devices to collect vitals, detect early deterioration, and alert care teams instantly. This role of AI in healthcare management systems creates proactive care capabilities that drive better patient outcomes.
• Administrative Efficiency
AI handles appointment scheduling, billing, claims adjudication, and coding through automation and NLP. This frees clinicians from tedious tasks, reduces coding errors, and optimises workflow efficiency—proving Benefits of AI in medical diagnosis and treatment extend to operations and revenue cycles.
Benefits Behind the Buzz
• Faster, More Accurate Diagnostics
One of the most groundbreaking advantages of artificial intelligence in healthcare is its ability to detect diseases earlier and with greater accuracy than traditional methods. AI algorithms trained on vast amounts of medical data can quickly identify patterns that even the most experienced radiologists might miss.
For instance, in oncology, AI models can detect subtle abnormalities in mammograms or CT scans—sometimes months before a human physician would. This early detection dramatically improves patient outcomes, as diseases like cancer are far more treatable in early stages. Additionally, AI systems reduce diagnostic errors, which are among the top causes of preventable harm in healthcare.
• Personalised Treatment Plans
AI healthcare solutions use machine learning and data analytics to create individualised care strategies based on each patient’s genetic makeup, lifestyle, medical history, and treatment response. This is a key development in the rise of precision medicine.
Rather than relying on a one-size-fits-all protocol, AI recommends therapies that are more likely to be effective for that particular individual. For example, AI can analyse genetic data to predict how a patient might metabolise a specific drug, enabling doctors to prescribe the right treatment at the right dose, reducing side effects and improving outcomes.
The benefits of AI in medical diagnosis and treatment are clear—it ensures that patients receive care tailored to their unique biology and condition.
• Operational Efficiency
Administrative overload has long been a burden on healthcare professionals. AI related to healthcare brings relief by automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, such as medical transcription, billing, scheduling, and insurance claims processing.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools can summarise patient visits, update electronic health records (EHRs), and assist in medical coding—freeing up doctors and nurses to spend more time with their patients. AI chatbots and virtual assistants handle patient enquiries and appointment bookings, reducing the workload on front-desk staff.
The result is a leaner, faster, and more efficient healthcare delivery model—where clinicians can refocus on delivering high-quality, personalised care.
• Cost Control and Financial Savings
Healthcare costs are skyrocketing worldwide. However, AI healthcare solutions help mitigate this crisis by streamlining operations, reducing unnecessary testing, and enabling early intervention.
For example, predictive analytics can identify high-risk patients before their condition worsens, preventing costly emergency interventions or hospitalisations. AI-driven diagnostic tools also reduce the need for redundant tests by increasing accuracy on the first attempt.
By eliminating inefficiencies and optimising resource allocation, AI not only saves time but also significantly cuts costs for both healthcare providers and patients.
• Enhanced Patient Experience
The role of AI in healthcare management systems goes beyond data and diagnostics—it fundamentally improves the way patients interact with the healthcare ecosystem.
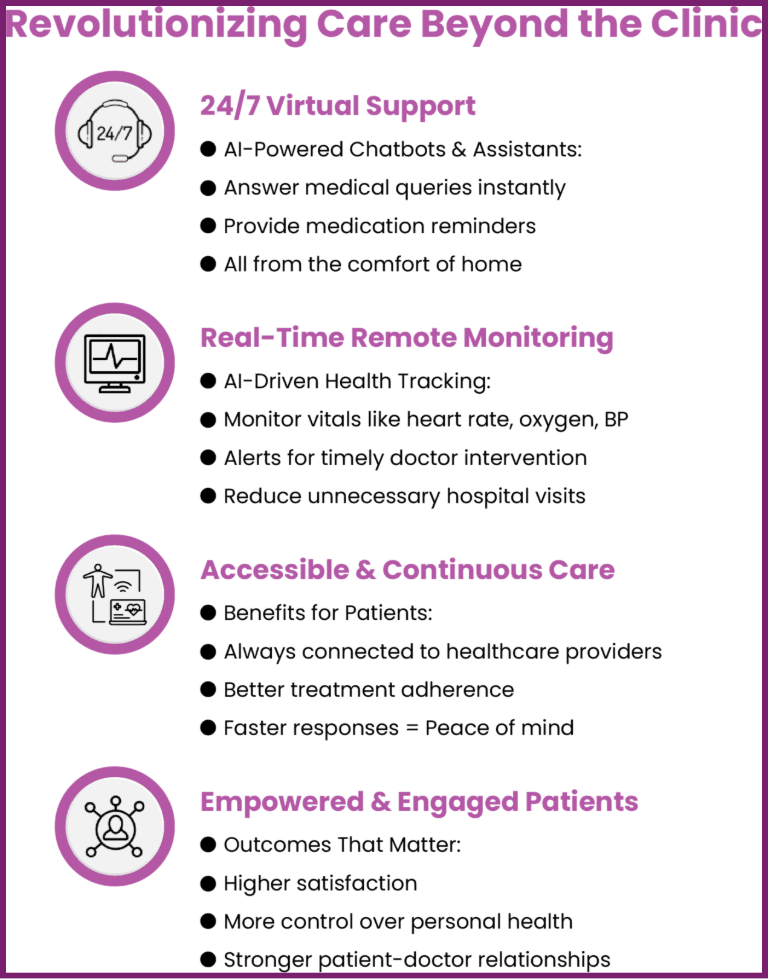
Virtual assistants and AI-powered chatbots provide 24/7 support, answering common medical queries, helping with medication reminders, or guiding patients through post-treatment care—all from the comfort of their home.
Remote patient monitoring tools allow doctors to track vitals in real time, offering timely interventions without the need for physical visits. These AI-driven enhancements ensure that care is continuous, accessible, and convenient, increasing patient satisfaction and compliance. As a result, patients feel more supported, engaged, and empowered throughout their healthcare journey.
Hurdles & Ethical Considerations in AI Healthcare Integration
While artificial intelligence in healthcare promises revolutionary benefits, it also introduces significant challenges that must be addressed to ensure responsible, ethical, and effective implementation. These hurdles span regulatory, technical, and human factors that influence the trust, adoption, and long-term reliability of AI in clinical settings.
1. Data Privacy and Security Compliance
One of the foremost concerns is patient data privacy. AI models require access to vast amounts of sensitive medical data, including electronic health records (EHRs), genetic information, and diagnostic images. This access makes healthcare systems vulnerable to data breaches and misuse. To mitigate risks, healthcare providers must strictly adhere to compliance frameworks like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the U.S. or GDPR in the EU. These regulations mandate how data can be collected, stored, and processed. Securing AI platforms with encryption, anonymization, and regular audits is crucial for maintaining patient trust and legal compliance.
2. Lack of Interpretability and Clinician Trust
Clinicians are less likely to rely on AI tools they don’t understand. Many advanced AI systems, particularly deep learning models, operate as “black boxes”—they provide results without clear explanations. This lack of transparency hinders clinical decision-making and can lead to reluctance among healthcare providers. To build trust, AI developers must create explainable AI (XAI) models that offer clear reasoning for their recommendations, ensuring they complement—rather than replace—clinical judgement.
3. Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating AI into existing healthcare IT infrastructures, especially EHR systems, poses technical difficulties. AI tools must be compatible with legacy software, meet interoperability standards, and work in real-time without disrupting existing workflows. This often requires additional investment in infrastructure and skilled IT support.
4. Staff Training and Workflow Adaptation
For AI to function effectively, healthcare professionals must understand how to use it. This necessitates comprehensive training programs that focus on tool functionality, interpretation of results, and ethical use. Institutions must also adjust workflows to accommodate AI insights while minimising disruptions in patient care.
5. Continuous Validation and Updates
Medical knowledge evolves rapidly. AI systems must undergo ongoing validation to ensure their recommendations remain relevant and aligned with the latest clinical guidelines. Static models risk becoming outdated, which can lead to inaccurate or harmful decisions. Continuous learning and regular updates are essential for maintaining AI accuracy and reliability in the healthcare environment.
Future of AI in Healthcare
• Telehealth expansion: AI powers smart triage, symptom checkers, and virtual clinical assistants.
• Predictive analytics: AI flags disease risks based on health history, guiding preventive care.
• Clinical decision support: Embedded AI within EHRs helps providers act promptly and accurately.
• Genomic medicine & mental health: AI analyses genetic and behavioural data for personalised mental health interventions.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence in healthcare revolutionises medicine by delivering faster diagnostics, personalised treatments, and operational efficiency. From machine learning imaging tools and NLP‑powered record analysis to AI‑driven remote monitoring and telehealth, these AI healthcare applications reimagine patient care at every level. While challenges remain in data security, clinician trust, and system integration, transparent algorithms and regulatory standards pave the way forward.
As AI present in the healthcare sector continues to mature, it empowers providers, pays off in cost benefits, and most importantly, enhances patient outcomes. Dive deeper to discover how AI shapes the future of medicine—and why this era may truly be its greatest innovation driver.





